NAT stands for Network Address Translation. In the NAT mode, the load balancer will route traffic between the user and server by changing the destination IP address of the packets.
TCP Connection Overview
TCP connection is established between the client and the server.
The load balancer just ensures a client is always forwarded to the same server.
Data Flow
As shown below, the clients get connected to the service VIP. The load balancer chooses a server in the pool and then forwards packets to it by changing the destination IP address.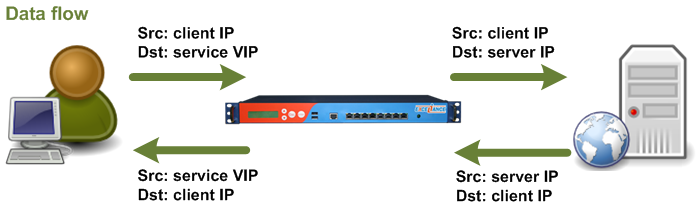 Read More:
Read More:
NAT Mode Pros & Cons
Pros
fast load balancing
easy to deploy
Cons
infrastructure intrusive: need to change the default gateway of the servers
The server default gateway must use the load balancer in order to do reverse NAT operation.
output bandwidth is limited by the load balancer's output capacity
When to Use This Architecture?
where response time matters
where no intelligence is required
when the output capacity of the load balancer won’t be a bottleneck in a near future
when nothing but the default gateway of the servers can be changed


