A decision-making framework breaking down the strengths, weaknesses and ideal use cases to help users choose the proper protocol for their systems.
Initially published in The New Stack
We often think of protocol choice as a purely technical decision, but it's a critical factor in the user experience and how your application is consumed. This is a high-impact business decision, making it crucial for the technical team to first understand the business situation and priorities.
Choosing the right transport protocol - TCP, UDP, or QUIC - has a profound impact on scalability, reliability, and performance. These protocols function like different postal services, each offering a unique approach to delivering messages across networks. Should your platform prioritize the reliability of a certified letter, the speed of a doorstep drop-off, or the innovation of a couriered package with signature confirmation?
This decision-making framework breaks down the strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases of TCP, UDP, and QUIC. It gives platform engineers and architects the insights to choose the proper protocol for their systems.
Overview of Protocols
Most engineers are familiar with TCP and have heard of UDP. Some may even have hands-on experience with QUIC. However, to make the right choice, it’s helpful to align on how these protocols compare before diving into the decision-making framework.
TCP: The Certified Letter
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is the traditional way to reliably send data while keeping a steady connection. It ensures that every packet arrives at its destination in order and without corruption.
Key Traits: Reliable, connection-oriented, ordered delivery.
Use Cases: File transfers, database queries, email, and transactional data.
Analogy: You send a certified letter and receive confirmation that it was delivered, but the process involves extra steps and time for those assurances.
For example, when downloading a file, TCP ensures that every byte is delivered. If packets are dropped, TCP will request retransmission and then reassemble them when the dropped packets are received, making it perfect for applications where data integrity is critical. The Internet was initially built on TCP, powering early protocols like HTTP/1.0 and FTP, and has been the leading protocol for a long time.
UDP: The Doorstep Drop-off
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is all about speed and simplicity. It skips the delivery guarantees and focuses instead on getting packets out as fast as possible. This speed comes at a cost, but in the right situations, it is worth it.
Key Traits: Lightweight, fast, connectionless, no delivery guarantees.
Use Cases: Real-time applications like video conferencing, gaming, and DNS queries.
Analogy: You drop a package on someone’s doorstep. It’s quick and easy, but you don’t know if or when it’ll be picked up.
UDP shines in scenarios where low latency is essential, and some data loss is acceptable – like a live-streamed sports match where missing a frame or two isn’t catastrophic. We are fine as long as most of the data is delivered.
QUIC: The Courier with Signature Confirmation
QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) is the new kid on the block, designed to combine UDP’s speed with added reliability, security, and efficiency. It’s the foundation of HTTP/3 and is optimized for latency-sensitive applications. One of its most important features is its ability to maintain connections even when users switch networks, such as moving from Wi-Fi to mobile data.
Key Traits: Built on UDP, encrypted by default, reliable delivery, and faster connection setup.
Use Cases: Modern web applications, secure microservices communication, and HTTP/3.
Analogy: You use a courier service that guarantees fast delivery and requires a signature. It’s both secure and efficient, ensuring the package reaches its destination reliably.
QUIC’s integration into HTTP/3 makes it a game-changer for web performance, reducing latency and connection overhead while improving security.
The Decision-Making Framework
Consider your application's specific needs when deciding on the right transport protocol. These can be grouped into four primary points.
Reliability
For applications where packet loss or data corruption cannot be tolerated, TCP or QUIC is the best choice. For example, financial applications or e-commerce platforms rely on complete and accurate data delivery to maintain transaction integrity. Both protocols are equally reliable.
TCP ensures that every packet reaches its destination as intended, albeit with some added latency. It is a very safe choice. In cases where reliability is essential but performance and low latency are also priorities, QUIC provides an excellent middle ground.
Speed
When low latency takes precedence over everything else, UDP becomes the preferred protocol. Applications like video conferencing, where real-time data transmission is vital, often rely on UDP. Losing a frame or two is an acceptable trade-off for maintaining a smooth and uninterrupted stream.
QUIC, while faster than TCP due to reduced connection overhead, adds encryption and reliability mechanisms on top of UDP, which introduces processing overhead.
Security
QUIC stands out for use cases that demand speed, reliability, and robust security. Modern web applications leveraging HTTP/3 benefit from QUIC's low-latency connections and built-in encryption, which makes it particularly valuable for mobile users or environments with unreliable network conditions.
Overhead
UDP has very low computational overhead, as it lacks complex error correction mechanisms, while TCP has moderate computational requirements. QUIC requires higher computational requirements than both TCP and UDP, primarily due to mandatory encryption and advanced congestion control features.
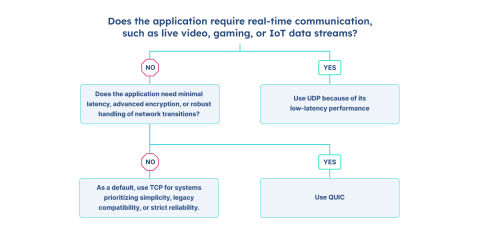
Decision Tree
Deciding on a protocol should be pretty easy at this point, but it is good to ask a few questions to help confirm the choice. These questions are particularly helpful when talking to stakeholders or decision-makers to validate your choices.
Does the application require real-time communication, such as live video, gaming, or IoT data streams?
If yes, use UDP because of its low-latency performance.
If no, continue.
Does the application need minimal latency, advanced encryption, or robust handling of network transitions?
If yes, use QUIC.
If no, continue.
As a default, use TCP for systems prioritizing simplicity, legacy compatibility, or strict reliability.
The Rise of QUIC
One clear thing is that QUIC seems to provide a “best of all worlds” solution. Truthfully, it is transforming how engineers think about transport protocols. Major players like Google and Cloudflare have already leveraged QUIC to great effect. As the core of HTTP/3, QUIC is faster than TCP and includes encryption.
However, adopting QUIC isn’t without challenges. Older systems and tools may need updates to fully support it. Platforms with legacy dependencies on TCP will need to carefully evaluate the cost and effort of transitioning. Remember that the internet was built on TCP and has been the standard for a long time.
At the same time, staying current with advancements like QUIC isn’t just about keeping up with trends. It’s about future-proofing your platform. If you can make the case for QUIC, it is an investment that will continue to pay off for a long time.

How HAProxy Supports TCP, UDP, and QUIC
HAProxy Enterprise delivers comprehensive support for TCP, UDP, and QUIC, making it the fastest and most efficient solution for managing traffic across diverse protocols. Here’s a closer look at how it handles each:
TCP Load Balancing
HAProxy operates as a TCP proxy, relaying TCP streams from clients to backend servers. This mode allows it to handle any higher-level protocol transported over TCP, such as HTTP, FTP, or SMTP. Additionally, it supports application-specific protocols like the Redis Serialization Protocol or MySQL database connections.
With fine-grained control over connection handling, timeouts, and retries, HAProxy ensures data integrity and reliability. It is an excellent choice for transactional systems and applications that depend on robust data delivery.
UDP Load Balancing with HAProxy Enterprise UDP Module
For UDP, HAProxy Enterprise extends its capabilities with a dedicated UDP module. This module introduces a specialized udp-lb configuration section for defining the address, port, and backend servers to relay traffic. It supports health checking and traffic logging, enhancing visibility and reliability.
UDP’s fire-and-forget nature makes it ideal for applications like DNS, syslog, NTP, or RADIUS, where low overhead is critical. HAProxy’s UDP module shines in scenarios requiring high throughput. However, it’s important to consider network conditions - UDP can outperform TCP in low-packet-loss environments but may struggle in congested networks due to its lack of congestion control.
QUIC and HTTP/3 Support
HAProxy supports QUIC as part of its integration with HTTP/3, delivering cutting-edge performance and user experience improvements. Unlike earlier HTTP versions that relied on TCP, HTTP/3 uses QUIC, a UDP-based protocol designed for speed, reliability, and security.
HAProxy Enterprise simplifies QUIC adoption with a preconfigured package and a compatible TLS library. The prepackaged setup eliminates the need for users to recompile HAProxy or source a specialized library like quictls, which is recommended for HAProxy Community Edition. While the Community Edition can use plain OpenSSL in a degraded mode (no 0-RTT support), specialized libraries provide enhanced functionality.
QUIC offers features such as:
Reduced Latency: Faster connection establishment and elimination of head-of-line blocking.
Built-in Security: Mandatory TLS 1.3 encryption for all communication.
Congestion Control Flexibility: Reliable, connection-oriented transport with more flexible congestion and flow control settings.
These features make QUIC and HTTP/3 ideal for modern web platforms and mobile applications where latency and seamless connections are top priorities.
With HAProxy Enterprise’s built-in support for these protocols, engineers can implement sophisticated, high-performance traffic management solutions quickly and effectively while leveraging advanced features like health checks, logging, and robust security measures.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the best transport protocol defines how your platform delivers value to its users - just like choosing the best method to send an important message. The certified reliability of TCP, the speed of UDP, or the modern efficiency of QUIC each have their place in the engineering toolkit. HAProxy Enterprise supports all these protocols and more with industry-leading performance and reliability.
Assess your current systems to ensure you are optimizing protocol choices for your platform’s specific needs. By understanding and applying these frameworks, you’ll be better equipped to design robust, scalable architectures that meet today’s challenges and tomorrow’s opportunities.
Subscribe to our blog. Get the latest release updates, tutorials, and deep-dives from HAProxy experts.